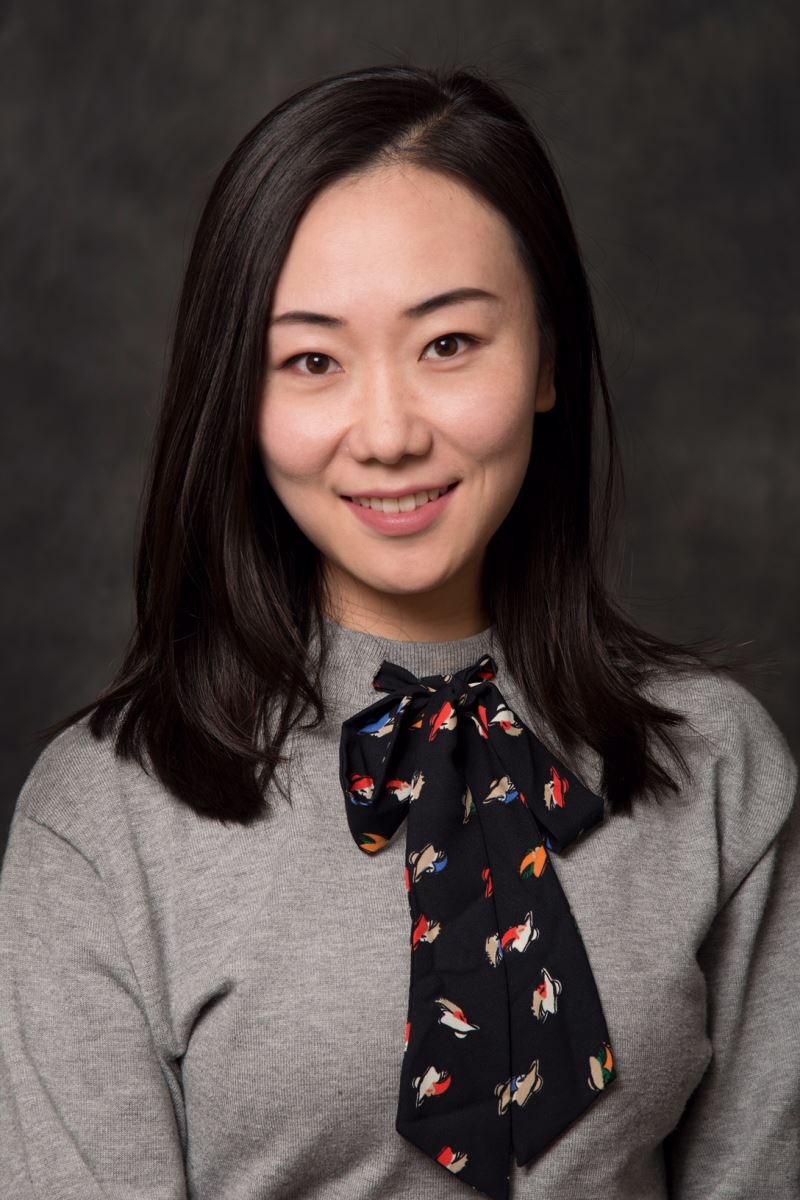

李鸞 長聘教軌助理教授
部門:本科生公共英語教學中心
郵箱:liluan@sjtu.edu.cn
 主要經歷
主要經歷
教育及工作經歷
- 意昂体育 助理教授
- 華東師範大學心理與認知科學意昂 博士後助理研究員
- 澳大利亞麥考瑞大學(Macquarie University)認知科學系 哲學博士
- 澳大利亞麥考瑞大學(Macquarie University)認知科學系 研究碩士
- 香港理工大學 中文及雙語學系 翻譯學碩士
- 西安外國語大學 高級翻譯意昂 文學學士
 教學科研
教學科研
研究方向
- 兒童語言認知發展
- 詞匯(語義🎋、語音✶、多維)網絡
- (語言等)模型與人類概念系統的對齊
- 閱讀習得
研究方法
- 心理和神經語言學實驗(行為、眼動、fMRI、EEG)
- 計算建模
- 數據庫
科研項目
- 國家社會科學基金青年項目,“基於詞匯語義網絡的兒童語義發展及數據庫研究”,2023-2027🧑🚒,主持,在研
- 上海市腦功能基因組學重點實驗室開放課題🎯,“語義網絡的發展研究”,2022-2023,主持,結項
- 國家自然科學基金面上項目🧑🏻🦰,“基於詞匯語義網絡的語義標準與語義整合的認知神經機製研究”🧘🏻,2020-2023🚛,參與,結項
- Australian Institute of Teaching and School Leadership Initial Teacher Education(澳大利亞國家教育與學校領導力研究所),“Reading instruction – Exemplar ITE program outlines”(閱讀教師培訓),2020-2021🔱,參與🫲🏽,結項
- Australia Research of Excellence Center in Cognition and Cognitive Disorders(澳大利亞認知與認知障礙國家研究中心)0️⃣,“Learning to read in bilingualism: Do English-Chinese bilingual children use different learning mechanisms in reading acquisition? ”(雙語閱讀),2019-2020♠︎,參與🍔,結項
科研成果(#一作 *通訊)
- Li, L.#, Song, M. #, Cai, Q.* (in press). The words children hear and see: Lexical diversity across-modalities and its impact on lexical development. https://osf.io/3a78s
- 李金彩#,李鸞 & 陶亮.(2024).語言知識探源:兒童與機器的語言知識從何而來?.自然辯證法通訊(11),1-11. DOI:10.15994/j.1000-0763.2024.11.001.
- Li, L.#, Hu, T. T., Liu, S. T.* (2024). Graded phonological neighborhood effects on lexical retrieval: Evidence from Mandarin Chinese. Journal of Memory and Language. (SSCI一區, IF = 4.74)
-
Yang, Y.#, Li, L. #, de Deyne, S., Li, B., Wang, J.*, & Cai, Q.* (2023). Unraveling lexical semantics in the brain: Comparing internal, external, and hybrid language models. Human Brain Mapping, 45(1), e26546, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.26546. (SCI一區🤸, IF = 5.038)
-
Wang, H. C.#*, Li, L., Rattanasone, N. X., Demuth, K., & Castles, A. (2023) Morphological effects on orthographic learning in monolingual English-speaking and bilingual Chinese-English-speaking children. Scientific Studies of Reading, 27(6), 557-569, DOI: 10.1080/10888438.2023.2217965. (SSCI一區🪦, IF = 4.9)
-
Li, L.#, Zhao, W.-T., Song, M., Wang, J. *, & Cai, Q.* (2023). CCLOOW: Chinese children’s lexicon of oral words. Behavior Research Methods. DOI: 10.3758/s13428-023-02077-6. (SSCI一區, IF = 7.867)
-
Li, L.#, Yang, Y., Song, M., Fang, S. Y., Zhang, M.Y., Chen, Q. R., & Cai, Q*. (2023). CCLOWW: A grade-level Chinese children’s lexicon of written words. Behavior Research Methods, 55(4), 1874-1889. DOI: 10.3758/s13428-022-01890-9. (SSCI一區👩🏼💼, IF = 7.867)
-
Wang, X.#*, Li, L., & McMurray, B. (2022). Cross-modal perceptual learning in learning a tonal language. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society (Vol. 44, No. 44).
-
Li, L.#*, Marinus, E., Castles, A., & Wang, H. C. (2021). Oral vocabulary affects children’s orthographic learning in Chinese. Reading and Writing, 34(6), 1369-1385. (SSCI二區🚛, IF = 3.208)
-
Li, L.#*, Marinus, E., Castles, A., Hsieh, M. L., & Wang, H. C. (2020). Semantic and phonological decoding in children’s orthographic learning in Chinese. Scientific Studies of Reading, 25(4), 319-334. (SSCI一區, IF = 4.9)
-
Li, L.#*, Marinus, E., Castles, A., Yu, L., and Wang, H.-C. (2019). Eye-tracking the effect of semantic decoding on orthographic learning in Chinese. PsyArXiv. DOI: 10.31234/osf.io/ekxd6.
-
Li, L.#*, Wang, H-C., Castles, A., Hsieh, M-L., and Marinus, E. (2018). Phonetic radicals, not phonological coding systems, support orthographic learning via self-teaching in Chinese. Cognition, 176, 184-194. (SSCI一區, IF = 4.079)
歡迎語言𓀖💒、心理📞🦪、計算、認神或教育學等背景的同學加入我們的研究項目。尤其歡迎對人類復雜語義概念系統感興趣,且喜歡跨學科🖋、想了解其它學科研究方法和視角、或者對科研成果轉化感興趣的同學👨。

 ENGLISH
ENGLISH 教師登錄
教師登錄
 地址:中國上海東川路800號意昂体育注册閔行校區楊詠曼樓
地址:中國上海東川路800號意昂体育注册閔行校區楊詠曼樓 郵編:200240
郵編:200240  網址:
網址: 電話🧍♀️:021-34205664 (黨政辦公室)
電話🧍♀️:021-34205664 (黨政辦公室) 